6/27/2024 Admin
Using a Blazor Excel Datasheet To Update A Database
Most business applications involve viewing, updating, and deleting data. To facilitate these actions developers using spend a lot of time and money creating forms.
In this blog post, we’ll explore how to use an Excel-like data editor control within a Blazor application, to update a SQL database, eliminating the need to create forms.
The Application
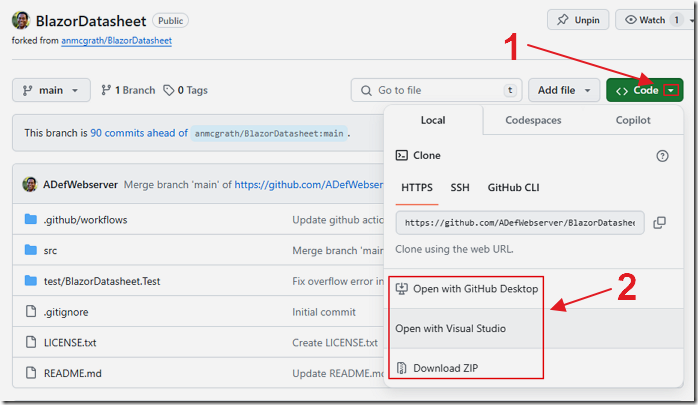
Download the application from: https://github.com/ADefWebserver/BlazorDatasheet
Note: This project is forked from: anmcgrath/BlazorDatasheet
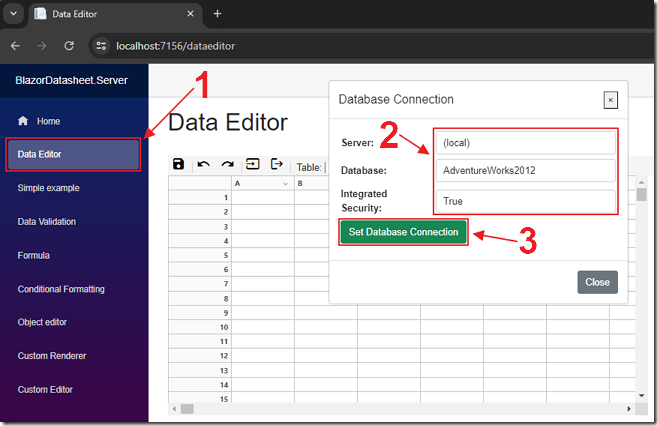
Run the program and select the Data Editor menu item.
The Data Editor will detect that there is no database connection, and the Database Connection dialog will automatically open.
Enter the connection information to a SQL database, and click the Set Database Connection button.
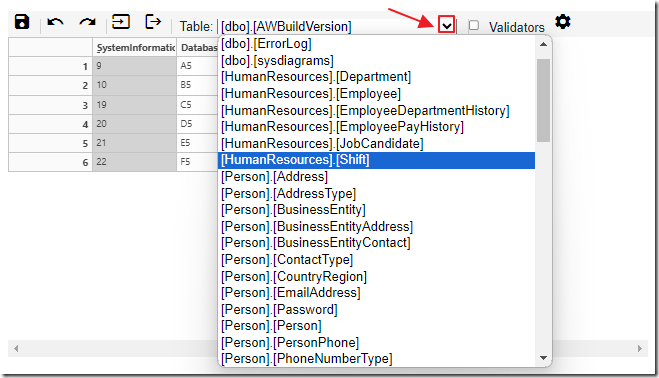
Once connected to the database, the Table dropdown, when expanded, will display all the tables in the database.
After selecting a table the data will display.
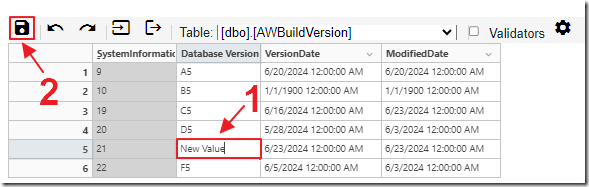
You can double click in any cell to enter edit mode to update the value.
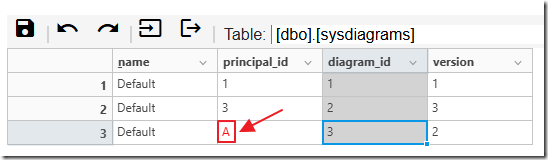
Note: Cells with a gray background are primary keys or auto number fields that cannot be edited.
Note: Database field types: uniqueidentifier, hierarchyid, varbinary, geography, and computed columns will not display.
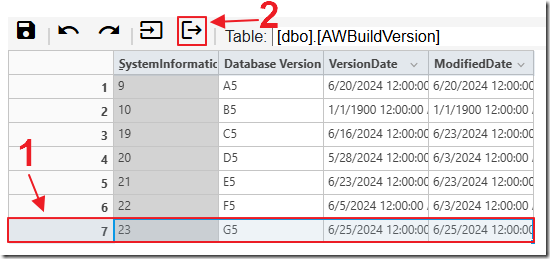
Clicking the Save button will save the changes to the database.
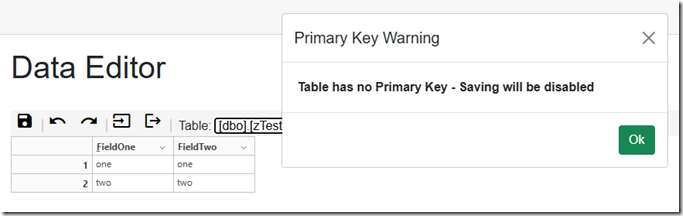
If a table does not have any primary keys a warning will display that saving will be disabled.
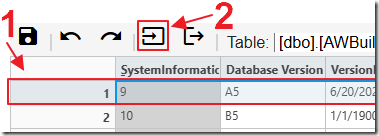
To add a record, first select a row in the table and then click the Insert Row button.
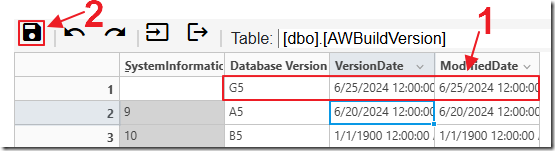
Enter new data in the row and click the Save button.
Note: Auto number fields do not require a value to be entered.
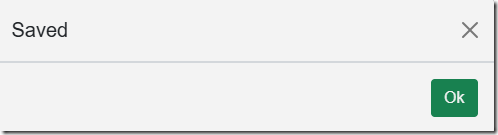
A Saved dialog will appear as a confirmation.
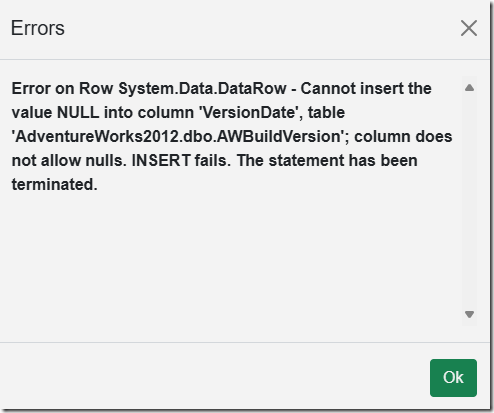
If the insert or update process encounters any errors they will be displayed.
To remove a record, select the row in the table and then click the Delete Row button.
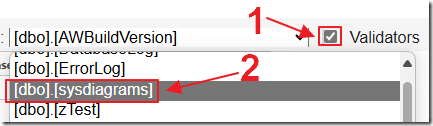
To enable validation, first check the Validators box then select a table.
Any values entered that violate the following rules will display in red:
- Only numbers allowed for integer values
- Text values cannot be longer then the field length in the database
The Code
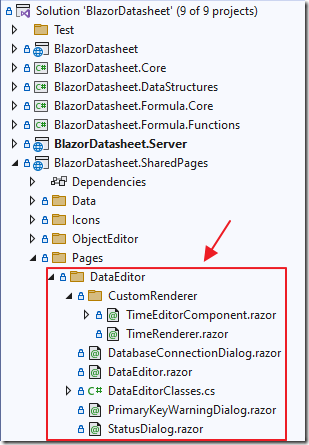
The image above shows the outline of the program structure.
The Data Editor consists of code added to the anmcgrath/BlazorDatasheet project.
The UI
The toolbar uses the following code:
<div class="rz-p-sm-1" style="background-color:whitesmoke;border-block:thin;border-block-color:lightgray;text-align:left"><button @onclick="btnSave" disabled="@SavingDisabled" style="background:none;border:none;"><i class="material-icons" style="color:black;">save</i></button><span style="border-right: 2px solid #D3D3D3;"></span><button @onclick="() => sheet.Commands.Undo()" title="Undo" style="background:none;border:none;"><i class="material-icons" style="color:black;">undo</i></button><button @onclick="() => sheet.Commands.Redo()" title="Redo" style="background:none;border:none;"><i class="material-icons" style="color:black;">redo</i></button><span style="border-right: 2px solid #D3D3D3;"></span><button @onclick="InsertRowAfterSelection" title="Insert Row" style="background:none;border:none;"><i class="material-icons" style="color:black;">input</i></button><button @onclick="RemoveRow" title="Delete Row" style="background:none;border:none;"><i class="material-icons" style="color:black;">logout</i></button><span style="border-right: 2px solid #D3D3D3;"></span><span> Table: </span><select @onchange="OnSelectedTableChanged" style="width: 300px; border-block:hidden">@foreach (var tableName in tableNames){<option value="@tableName">@tableName</option>}</select><span> </span><span style="border-right: 2px solid #D3D3D3;"></span><input type="checkbox" @bind="UseValidation" id="CheckBoxValidation" /><label for="CheckBoxValidation" style="margin-left: 8px; vertical-align: middle;">Validators</label><button @onclick="OpenShowConnectionDialog" title="Settings" style="background:none;border:none;"><i class="material-icons" style="color:black;">settings</i></button></div>
The data table uses the following markup:
<Datasheet @ref="_datasheet"CustomCellTypeDefinitions="CustomTypes"Sheet="sheet"Virtualise="true"CanUserMergeRows="false"ShowColHeadings="true"ShowRowHeadings="true"CanUserInsertRows="true"CanUserRemoveRows="true"CanUserInsertCols="false"CanUserRemoveCols="false"CanUserSort="false" /></div>
Loading Data
When a table is selected in the dropdown the LoadTableData method is called that performs the following functions:
-
Retrieve Table Metadata:
- Fetch primary keys using
GetPrimaryKeyand computed columns withGetComputedColumns.
- Fetch primary keys using
-
Fetch and Filter Column Details:
- Retrieve column details for
selectedTableand populateTableColumns. - Filter out unwanted column types:
uniqueidentifier,hierarchyid,varbinary,geography, and computed columns.
- Retrieve column details for
-
Build SQL Query:
- Convert
TableColumnsto a comma-separated string of column names. - Construct the SQL query:
- If no primary keys, disable saving, show a warning, and create a query without primary key ordering.
- If primary keys exist, create a query with
ROW_NUMBER()ordering by primary keys.
- Convert
-
Execute SQL Query and Handle Data:
- Use
SqlDataAdapterto fill aDataTable(dt). - Save a copy of
dtasOriginalDataTable.
- Use
-
Add
_IdColumn:- Insert
_Idas the first column inTableColumns. This is used to determine if a row is new or is later deleted.
- Insert
-
Load Data into Sheet:
- Call
LoadTableHeadersAndDatawithTableColumnsanddt.
- Call
private void LoadTableData(string paramSelectedTable){ErrorMessage = "";selectedTable = paramSelectedTable;isLoading = true;StateHasChanged();// Use the DatabaseConnectionString to get the data from the selected tableusing (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(DatabaseConnectionString)){connection.Open();try{// Clear the list of changed rowsColChangedRows = new List<int>();// Get the primary keys for the tablePrimaryKeys = GetPrimaryKey(connection, selectedTable);// Get the computed columns for the tableList<string> ComputedColumns = GetComputedColumns(connection, selectedTable);// Get a list of the column namesTableColumns = new List<DTODatabaseColumn>();DataTable Columns = connection.GetSchema("Columns");foreach (DataRow row in Columns.Rows){if ($"[{row["TABLE_SCHEMA"].ToString()}].[{row["TABLE_NAME"].ToString()}]" == selectedTable){DTODatabaseColumn objTableColumns = new DTODatabaseColumn();objTableColumns.ColumnName = row["COLUMN_NAME"].ToString();objTableColumns.ColumnType = row["DATA_TYPE"].ToString();if (row["CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH"] != DBNull.Value){objTableColumns.ColumnLength = Convert.ToInt32(row["CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH"]);}else{objTableColumns.ColumnLength = 0;}if (PrimaryKeys.Contains(row["COLUMN_NAME"].ToString())){objTableColumns.IsPrimaryKey = true;}else{objTableColumns.IsPrimaryKey = false;}TableColumns.Add(objTableColumns);}}// Remove from TableColumns any colums types of unique identifiersTableColumns = TableColumns.Where(x => x.ColumnType != "uniqueidentifier").ToList();// Remove from TableColumns any colums types of hierarchyidTableColumns = TableColumns.Where(x => x.ColumnType != "hierarchyid").ToList();// Remove from TableColumns any colums types of varbinaryTableColumns = TableColumns.Where(x => x.ColumnType != "varbinary").ToList();// Remove from TableColumns any colums types of geographyTableColumns = TableColumns.Where(x => x.ColumnType != "geography").ToList();// Remove from TableColumns any colums types of computed// remove colums conatined in the ComputedColumns listTableColumns = TableColumns.Where(x => !ComputedColumns.Contains(x.ColumnName)).ToList();// Get Table names from TableColumns as comma seperated valuesstring strTableNames = string.Join(",", TableColumns.Select(x => $"[{x.ColumnName}]").ToArray());string sql = "";// See if there are any primary keysif (PrimaryKeys.Count == 0){SavingDisabled = true;ShowPrimaryKeyWarningDialog();// Get the data from the selected tablesql = $"SELECT 0 AS _Id, {strTableNames} FROM {selectedTable}";}else{SavingDisabled = false;// Turn PrimaryKeys into a comma seperated stringstring strPrimaryKeys = string.Join(",", PrimaryKeys.Select(x => $"[{x}]").ToArray());// Get the data from the selected tablesql = $"SELECT ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY {strPrimaryKeys}) AS _Id, {strTableNames} FROM {selectedTable}";}SqlDataAdapter adapter = new SqlDataAdapter(sql, connection);DataTable dt = new DataTable();adapter.Fill(dt);connection.Close();// Save the original dataOriginalDataTable = dt.Copy();// Make the first column _IdTableColumns.Insert(0, new DTODatabaseColumn { ColumnName = "_Id", ColumnType = "int", ColumnLength = 0, IsPrimaryKey = true });// Load Data into the DatasheetLoadTableHeadersAndData(TableColumns, dt);}catch (Exception ex){ErrorMessage = ex.GetBaseException().Message;if (connection.State == ConnectionState.Open){connection.Close();}isLoading = false;StateHasChanged();}}isLoading = false;StateHasChanged();}
This calls the LoadTableHeadersAndData method that does the following:
-
Create Sheet:
- Create a new sheet with a number of rows and columns based on the input
paramDataTableandparamDatabaseColumns.
- Create a new sheet with a number of rows and columns based on the input
-
Turn Off History:
- Disable history tracking for batch updates to improve performance during initial setup.
-
Hide
_IdColumn:- Hide the first column (
_Id)
- Hide the first column (
-
Set Column Headings and Types:
- Loop through
paramDatabaseColumnsto set column headings and cell types. - Use the
ColumnRegionclass to specify the region for column types and validators. - (If enabled) Apply different validators based on column type and length:
- Integer Validator for columns containing “int”.
- Length Validator for columns with specified lengths and types containing “char”.
- Loop through
-
Load Data into Sheet:
- Loop through
paramDataTable.Rowsto load data into the sheet cells. - Set cell values using a helper function
GetCellValuethat handles data type conversion. - If the column is a primary key, set the cell to read-only and change the background color to light grey.
- Loop through
-
Wire Up Event Handlers:
- Cell Changes: Attach a method to handle cell changes (
CellChanged). - Row Changes: Attach a method to handle row deletions. Prevent deletion of the last row by inserting a new row if necessary.
- Cell Changes: Attach a method to handle cell changes (
-
Turn On History:
- Re-enable history tracking after batch updates are complete
private void LoadTableHeadersAndData(List<DTODatabaseColumn> paramDatabaseColumns, DataTable paramDataTable){// Create sheet with the number of columnssheet = new Sheet(paramDataTable.Rows.Count, paramDatabaseColumns.Count);// Turn off historysheet.BatchUpdates();sheet.Commands.PauseHistory();// Hide the _Id columnsheet.Columns.Hide(0, 0);int i = 0;foreach (DTODatabaseColumn objDatabaseColumn in paramDatabaseColumns){// Set the column headingssheet.Columns.SetHeadings(i, i, objDatabaseColumn.ColumnName);// Set the column typessheet.Cells.SetType(new ColumnRegion(i), objDatabaseColumn.ColumnType);if (UseValidation){// Integer Validatorif (objDatabaseColumn.ColumnType.Contains("int")){sheet.Validators.Add(new ColumnRegion(i), new NumberValidator(false));}// Length Validatorif (objDatabaseColumn.ColumnLength > 0){if (objDatabaseColumn.ColumnType.Contains("char")){sheet.Validators.Add(new ColumnRegion(i), new LengthValidator(objDatabaseColumn.ColumnLength, true));}}}i++;}// Load the data into the sheetint ii = 0;foreach (DataRow dataRow in paramDataTable.Rows){i = 0;foreach (DTODatabaseColumn objDatabaseColumn in paramDatabaseColumns){// Set the cell valuesheet.Cells[ii, i].Value = GetCellValue(dataRow[i].ToString(), objDatabaseColumn.ColumnType);if (objDatabaseColumn.IsPrimaryKey){// Set the cell to read only if it is a primary keysheet.Cells[ii, i].Format = new CellFormat() { IsReadOnly = true, BackgroundColor = "lightgrey" };}i++;}ii++;}// Wire up a method to catch cell changessheet.Cells.CellsChanged += CellChanged;// Wire up a method to catch row changes// Do not allow the last row to be deletedsheet.Rows.Removed += (sender, args) =>{// Turn off historysheet.BatchUpdates();sheet.Commands.PauseHistory();if (sheet.NumRows == 0){sheet.Rows.InsertAt(0);}// Turn off historysheet.EndBatchUpdates();sheet.Commands.ResumeHistory();};// Turn on historysheet.EndBatchUpdates();sheet.Commands.ResumeHistory();}
Save Data
When any cell is updated, the CellChanged method is called. In it, we capture the hidden _Id value for the row into a collection called ColChangedRows:
private void CellChanged(object sender, CellDataChangedEventArgs args){// Only add the row if one cell is changedif ((args.Positions.Count() > 0) && (args.Positions.Count() < 2)){// Get the row numberint row = Convert.ToInt32(args.Positions.FirstOrDefault().row);// Use that row number to get the hidden _Id valueint _Id = Convert.ToInt32(sheet.Cells[row, 0].Value);// Add the row to the list of changed rowsColChangedRows.Add(_Id);}}
We do this so that we don’t have to update the entire Datasheet.
When the Save button is clicked the following method executes:
private void SaveData(){// # Get the current data in the sheetcolGeneralErrors = new List<string>();// Initialize a new DataTableCurrentDataTable = new DataTable();// Define columns based on TableColumnsforeach (var column in TableColumns){CurrentDataTable.Columns.Add(new DataColumn(column.ColumnName, GetColumnType(column.ColumnType)));}// Populate the DataTable with rows from the sheetfor (int i = 0; i < sheet.NumRows; i++){DataRow row = CurrentDataTable.NewRow();for (int j = 0; j < TableColumns.Count; j++){try{if ((sheet.Cells[i, j].Value != null) && (sheet.Cells[i, j].Value != DBNull.Value)){if (CurrentDataTable.Columns[j].DataType.FullName == "System.Int32"){if (sheet.Cells[i, j]?.Value?.ToString() == ""){row[j] = DBNull.Value;}else{row[j] = Convert.ToInt32(sheet.Cells[i, j].Value);}}else if (CurrentDataTable.Columns[j].DataType.FullName == "System.DateTime"){if (sheet.Cells[i, j]?.Value?.ToString() == ""){row[j] = DBNull.Value;}else{row[j] = Convert.ToDateTime(sheet.Cells[i, j].Value);}}else if (CurrentDataTable.Columns[j].DataType.FullName == "System.TimeSpan"){if (sheet.Cells[i, j]?.Value?.ToString() == ""){row[j] = DBNull.Value;}else{var TimeSpanValue = sheet.Cells[i, j].Value.ToString();if (DateTime.TryParse(TimeSpanValue, out var parsedDateTime)){row[j] = parsedDateTime.TimeOfDay.ToString();}else if (TimeSpan.TryParse(TimeSpanValue, out var parsedTimeSpan)){row[j] = parsedTimeSpan;}else{row[j] = TimeSpanValue;}}}else{string currentValue = "";currentValue = sheet.Cells[i, j].Value?.ToString() ?? "";currentValue = currentValue.Replace("\r\n", " ").Replace("\t", " ").Replace("\r", " ").Replace("\n", " ").Trim();row[j] = currentValue;}}else{row[j] = CurrentDataTable.Columns[j].DefaultValue;}}catch (Exception ex){colGeneralErrors.Add(ex.GetBaseException().Message);}}CurrentDataTable.Rows.Add(row);}ProcessChanges();}
The ProcessChanges method performs the Updates, Inserts, and Deletions.
public void ProcessChanges(){try{// *****************************************// Updates// *****************************************ProcessUpdatedRows();// *****************************************// Inserts// *****************************************ProcessInsertedRows();// *****************************************// Deletes// *****************************************ProcessDeletedRows();}catch (Exception ex){colGeneralErrors.Add(ex.GetBaseException().Message);}ShowStatusDialog();}
Update Data
The ProcessUpdatedRows does the following:
-
Processing Each Changed Row:
foreach (int row in ColChangedRows)- Iterates over each unique row ID in
ColChangedRows.
- Iterates over each unique row ID in
-
Skipping Invalid Rows:
if (row == 0) continue;- Skips processing if the row ID is
0.
- Skips processing if the row ID is
-
Retrieving Current Data Row:
DataRow rowCur = CurrentDataTable.Select($"_Id = {row}").FirstOrDefault();- Selects the first row from
CurrentDataTablewhere_Idmatches the current row ID.
- Selects the first row from
-
Initializing Lists for SQL Statements and Parameters:
- Initializes
colSQLUpdateColumns,colSQLWhereColumns, andparametersas empty lists.
- Initializes
-
Building SQL Update and Where Clause Lists:
- Iterates over each column in
TableColumnsstarting from index1(assumes index0is_Id).- Retrieves column details:
columnName,columnType, andcolumnLength. - Sanitizes the parameter name by replacing spaces with underscores.
- Gets the value for the current column from
rowCur.
- Retrieves column details:
- Iterates over each column in
-
Adding Primary Key Columns to WHERE Clause:
- If the column is a primary key:
- Adds to
colSQLWhereColumns. - Creates a corresponding
SqlParameterwith the_wheresuffix.
- Adds to
- If the column is a primary key:
-
Adding Non-Primary Key Columns to UPDATE Clause:
- If the column is not a primary key:
- Adds to
colSQLUpdateColumns. - Creates a corresponding
SqlParameter.
- Adds to
- If the column is not a primary key:
-
Executing SQL Update Command:
- If there are columns to update (
colSQLUpdateColumns.Any()):- Constructs the
UPDATESQL statement withSETandWHEREclauses. - Opens a SQL connection using
DatabaseConnectionString. - Executes the
UPDATEcommand with the constructed SQL and parameters. - Catches and logs any exceptions that occur during execution.
- Ensures the SQL connection is closed after execution.
- Constructs the
- If there are columns to update (
private void ProcessUpdatedRows(){// Remove duplicate changed rowsColChangedRows = ColChangedRows.Distinct().ToList();// Process each changed rowforeach (int row in ColChangedRows){// Skip rows where _Id column is 0 or nullif (row == 0)continue;// Get row from CurrentDataTable where _Id matchesDataRow rowCur = CurrentDataTable.Select($"_Id = {row}").FirstOrDefault();var colSQLUpdateColumns = new List<string>();var colSQLWhereColumns = new List<string>();var parameters = new List<SqlParameter>();// Build SQL update and where clause listsfor (int i = 1; i < TableColumns.Count; i++){string columnName = TableColumns[i].ColumnName;string columnType = TableColumns[i].ColumnType;int columnLength = TableColumns[i].ColumnLength;// Sanitize parameter namestring paramName = columnName.Replace(" ", "_");object columnValue = rowCur[i] != DBNull.Value ? rowCur[i] : DBNull.Value;if (PrimaryKeys.Contains(columnName)){colSQLWhereColumns.Add($"[{columnName}] = @{paramName}_where");SqlParameter objSqlParameter = new SqlParameter();objSqlParameter.ParameterName = $"@{paramName}_where";objSqlParameter.Value = GetCellValue(columnValue, columnType);objSqlParameter.SqlDbType = GetSQLParameterType(columnType);parameters.Add(objSqlParameter);}else{colSQLUpdateColumns.Add($"[{columnName}] = @{paramName}");SqlParameter objSqlParameter = new SqlParameter();objSqlParameter.ParameterName = $"@{paramName}";objSqlParameter.Value = GetCellValue(columnValue, columnType);objSqlParameter.SqlDbType = GetSQLParameterType(columnType);parameters.Add(objSqlParameter);}}if (colSQLUpdateColumns.Any()){string updateSQL = string.Join(",", colSQLUpdateColumns);string whereSQL = string.Join(" AND ", colSQLWhereColumns);using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(DatabaseConnectionString)){try{connection.Open();string sql = $"UPDATE {selectedTable} SET {updateSQL} WHERE {whereSQL}";using (SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sql, connection)){command.Parameters.AddRange(parameters.ToArray());command.ExecuteNonQuery();}}catch (Exception ex){colGeneralErrors.Add($"Error on Row {row} - {ex.GetBaseException().Message}");}finally{if (connection.State == ConnectionState.Open){connection.Close();}}}}}}
Add Data
Data is added using ProcessInsertedRows:
-
Finding Added Rows:
var addedRows = CurrentDataTable.AsEnumerable().Where(row => row.Field<object>("_Id") == null).ToList();- Identifies rows in
CurrentDataTablewhere the_Idfield isnull(indicating newly added rows) and stores them in theaddedRowslist.
- Identifies rows in
-
Getting Identity Columns:
List<string> colIdentityColumns = new List<string>();- Initializes an empty list to store identity columns.
using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(DatabaseConnectionString))- Opens a SQL connection using
DatabaseConnectionString. - Retrieves identity columns using the
GetIdentityColumnsmethod. - Closes the connection in the
finallyblock to ensure it is closed even if an error occurs.
- Opens a SQL connection using
-
Looping Through Added Rows:
foreach (var rowCur in addedRows)- Iterates over each newly added row.
-
Initializing Lists for SQL Statements and Parameters:
- Initializes
colSQLUpdateColumnsandparametersas empty lists.
- Initializes
-
Building SQL Insert Columns and Parameters:
- Iterates over each column in
TableColumnsstarting from index1(assumes index0is_Id).- Checks if the column is not an identity column.
- Retrieves column details:
columnNameandcolumnType. - Sanitizes the parameter name by replacing spaces with underscores.
- Adds the column name to
colSQLUpdateColumns. - Retrieves the value for the current column from
rowCur. - Creates a corresponding
SqlParameter.
- Iterates over each column in
-
Executing SQL Insert Command:
- If there are columns to insert (
colSQLUpdateColumns.Any()):- Constructs the
INSERTSQL statement with column names and parameter names. - Opens a SQL connection using
DatabaseConnectionString. - Executes the
INSERTcommand with the constructed SQL and parameters. - Catches and logs any exceptions that occur during execution.
- Ensures the SQL connection is closed after execution.
- Constructs the
- If there are columns to insert (
private void ProcessInsertedRows(){// Find Added Rowsvar addedRows = CurrentDataTable.AsEnumerable().Where(row => row.Field<object>("_Id") == null).ToList();// Get the identity columnsList<string> colIdentityColumns = new List<string>();using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(DatabaseConnectionString)){try{connection.Open();colIdentityColumns = GetIdentityColumns(connection, selectedTable);}finally{if (connection.State == ConnectionState.Open){connection.Close();}}}// Loop through the added rowsforeach (var rowCur in addedRows){var colSQLUpdateColumns = new List<string>();var parameters = new List<SqlParameter>();// Loop through the columns, skipping the _Id columnfor (int i = 1; i < TableColumns.Count; i++){if (!colIdentityColumns.Contains(TableColumns[i].ColumnName)){string columnName = TableColumns[i].ColumnName;string columnType = TableColumns[i].ColumnType;// Sanitize parameter namestring paramName = columnName.Replace(" ", "_");colSQLUpdateColumns.Add($"[{columnName}]");object columnValue = rowCur[i] != DBNull.Value && rowCur[i] != null ? rowCur[i] : DBNull.Value;SqlParameter objSqlParameter = new SqlParameter();objSqlParameter.ParameterName = $"@{paramName}";objSqlParameter.Value = columnValue;objSqlParameter.SqlDbType = GetSQLParameterType(columnType);parameters.Add(objSqlParameter);}}if (colSQLUpdateColumns.Any()){string updateSQLColumns = string.Join(",", colSQLUpdateColumns);string parameterNames = string.Join(",", parameters.Select(p => p.ParameterName));using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(DatabaseConnectionString)){try{connection.Open();string sql = $"INSERT INTO {selectedTable} ({updateSQLColumns}) VALUES ({parameterNames})";using (SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sql, connection)){command.Parameters.AddRange(parameters.ToArray());command.ExecuteNonQuery();}}catch (Exception ex){colGeneralErrors.Add($"Error on Row {rowCur} - {ex.GetBaseException().Message}");}finally{if (connection.State == ConnectionState.Open){connection.Close();}}}}}}
Delete Data
-
Retrieve Non-null
_IdValues:- Filter
CurrentDataTableto get rows where_Idis not null. - Extract
_Idvalues into a list calledcurrentIds.
- Filter
-
Convert
_IdValues to Long:- Convert
currentIds(originally of typeint) to a list of long values calledlongCurrentIds.
- Convert
-
Identify Deleted Rows:
- Filter
OriginalDataTableto get rows whose_Idvalues are not present inlongCurrentIds.
- Filter
-
Process Each Deleted Row:
- Initialize
colSQLWhereColumnsfor the SQL WHERE clause andparametersfor SQL parameters.
- Initialize
-
Loop Through Columns:
- Skip the
_Idcolumn and iterate through the rest. - For primary key columns:
- Add an SQL condition to
colSQLWhereColumns. - Create a
SqlParameterwith the column value and add it toparameters.
- Add an SQL condition to
- Skip the
-
Execute Delete Command:
- If there are conditions in
colSQLWhereColumns, form the SQL DELETE command. - Open a database connection.
- Prepare and execute the SQL DELETE command using
SqlCommandwith the specified parameters.
- If there are conditions in
-
Handle Exceptions:
- Catch and log any exceptions, adding error details to
colGeneralErrors. - Ensure the database connection is closed after each operation.
- Catch and log any exceptions, adding error details to
private void ProcessDeletedRows(){// Get all the _Id values from CurrentDataTable that are not nullvar NotNullTableCollection = CurrentDataTable.AsEnumerable().Where(row => row.Field<object>("_Id") != null).ToList();// Get the _Id values from the CurrentDataTablevar currentIds = NotNullTableCollection.AsEnumerable().Select(r => r.Field<int>("_Id")).ToList();// Convert currentIds to longList<long> longCurrentIds = currentIds.Select(x => (long)x).ToList();// Filter OriginalDataTable to get the rows// that are not present in CurrentDataTablevar deletedRows = OriginalDataTable.AsEnumerable().Where(row => !longCurrentIds.Contains(row.Field<long>("_Id")));// Loop through the deleted rowsforeach (var rowCur in deletedRows){var colSQLWhereColumns = new List<string>();var parameters = new List<SqlParameter>();// Loop through the columns, skipping the _Id columnfor (int i = 1; i < TableColumns.Count; i++){string columnName = TableColumns[i].ColumnName;string columnType = TableColumns[i].ColumnType;// Sanitize parameter namestring paramName = columnName.Replace(" ", "_");object columnValue = rowCur[i] != DBNull.Value && rowCur[i] != null? rowCur[i]: DBNull.Value;if (PrimaryKeys.Contains(columnName)){colSQLWhereColumns.Add($"[{columnName}] = @{paramName}");SqlParameter objSqlParameter = new SqlParameter();objSqlParameter.ParameterName = $"@{paramName}";objSqlParameter.Value = columnValue;objSqlParameter.SqlDbType = GetSQLParameterType(columnType);parameters.Add(objSqlParameter);}}if (colSQLWhereColumns.Any()){string whereSQL = string.Join(" AND ", colSQLWhereColumns);using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(DatabaseConnectionString)){try{connection.Open();string sql = $"DELETE FROM {selectedTable} WHERE {whereSQL}";using (SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sql, connection)){command.Parameters.AddRange(parameters.ToArray());command.ExecuteNonQuery();}}catch (Exception ex){colGeneralErrors.Add($"Error on Row {rowCur} - {ex.GetBaseException().Message}");}finally{if (connection.State == ConnectionState.Open){connection.Close();}}}}}}
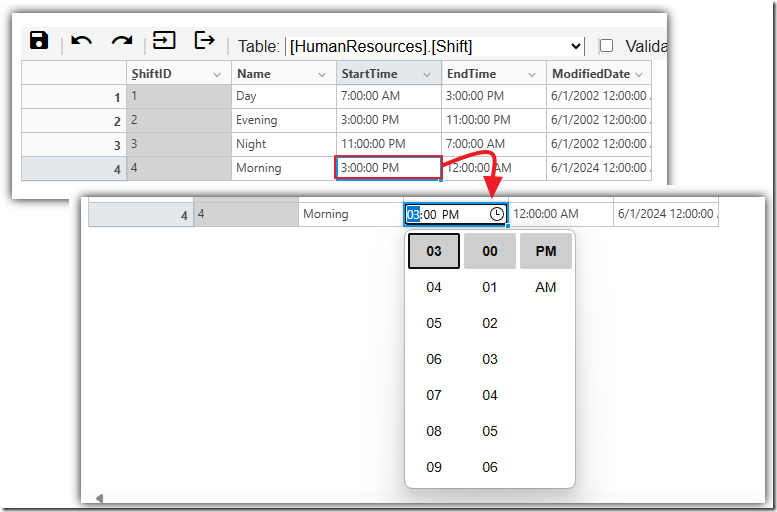
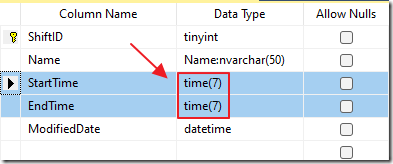
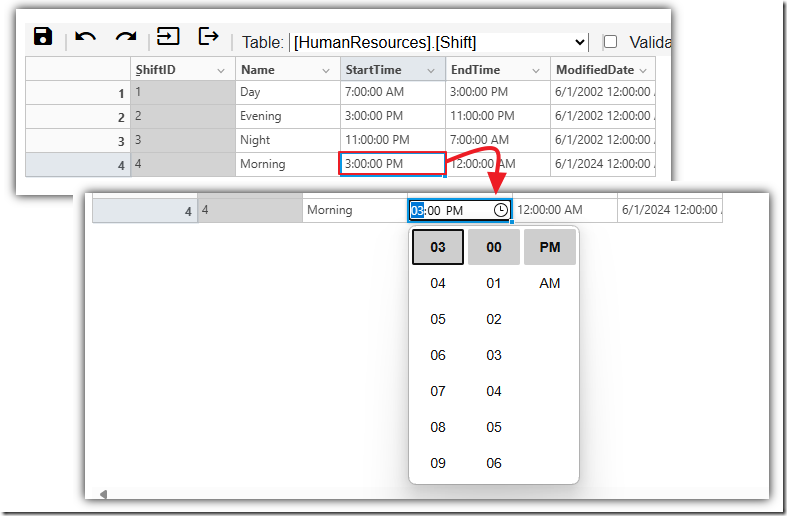
Custom Renderer and Custom Editor
Sometimes you are faced with a field type that does not work well with the standard cell editing formats of text or date.
It is possible to implement a Custom Renderer and a Custom Editor, such as the following, that only edits and displays time rather than time and date.
The first step is to create an editor control that inherits from BaseEditor like this:
@using BlazorDatasheet.Edit@using BlazorDatasheet.Util@using BlazorDatasheet.Core.Interfaces@using BlazorDatasheet.Core.Data@using BlazorDatasheet.Core.Edit@inherits BaseEditor<input type="time"class="date-input"@bind="currentDateTimeProperty"@bind:event="oninput"style="@Style; width: 100%;"@ref="InputRef" />@code {private IReadOnlyCell Cell { get; set; }private TimeOnly? currentTime;public TimeOnly? CurrentTime{get => currentTime;set{if (currentTime != value){currentTime = value;// Set currentDateTime// This gets the date part with time set to 00:00:00DateTime dateTime = DateTime.Now.Date;if (currentTime.HasValue){// Combine DateTime and TimeOnly to get a complete DateTimecurrentDateTime = dateTime.AddHours(currentTime.Value.Hour).AddMinutes(currentTime.Value.Minute).AddSeconds(currentTime.Value.Second);}}}}private DateTime currentDateTime;public DateTime currentDateTimeProperty{get => currentDateTime;set{if (currentDateTime != value){currentDateTime = value;if (TimeOnly.TryParse(currentDateTime.ToShortTimeString(), out var timeOnly)){currentTime = timeOnly;}else{currentTime = null;}}this.OnValueChanged.InvokeAsync(value.TimeOfDay.ToString());}}public override void BeforeEdit(IReadOnlyCell cell, Sheet sheet){Cell = cell;}public override void BeginEdit(EditEntryMode entryMode, string? editValue, string key){var canParse = DateTime.TryParse(editValue?.ToString(), out var parsedDateTime);if (canParse){currentDateTimeProperty = parsedDateTime;}else{currentDateTimeProperty = DateTime.Now;}}}
The next step is to create a renderer that inherits from BaseRenderer like this:
@inherits BlazorDatasheet.Render.BaseRenderer<span>@CurrentTime</span>@code {private string? CurrentTime{get{if (Cell.Value is DateTime dateTime){return dateTime.ToLongTimeString();}else{if (Cell.Value is TimeSpan timeSpan){// This gets the date part with time set to 00:00:00DateTime CurrentDateTime = DateTime.Now.Date;// Combine DateTime and timeSpan to get a complete DateTimeCurrentDateTime = CurrentDateTime.AddHours(timeSpan.Hours).AddMinutes(timeSpan.Minutes).AddSeconds(timeSpan.Seconds);return CurrentDateTime.ToLongTimeString();}return Cell.Value?.ToString();}}}}
Next, in the page that contains your Datasheet control, add a collection of CustomTypes of CellTypeDefintion like this:
private Dictionary<string, CellTypeDefinition> CustomTypes { get; } = new();
In the OnInitializedAsync method add editor and renderer to the CustomTypes like this:
CustomTypes.Add("time", CellTypeDefinition.Create<TimeEditorComponent, TimeRenderer>());
Add the CustomTypes to the Datasheet control like this:
<Datasheet @ref="_datasheet"CustomCellTypeDefinitions="CustomTypes"Sheet="sheet"Virtualise="true"CanUserMergeRows="false"ShowColHeadings="true"ShowRowHeadings="true"CanUserInsertRows="true"CanUserRemoveRows="true"CanUserInsertCols="false"CanUserRemoveCols="false"CanUserSort="false" />
Finally, you can set a cell to use the editor and renderer like this:
sheet.Cells[2, 2].Type = "time";
Incorporating AI
Watch the YouTube vide at this link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sKNHlM6GdCc
As covered in “Using OpenAI to Update A Blazor Excel Worksheet” an AI can be used to update data based on rules it infers from data edits you make.
Here’s a summary of the article:
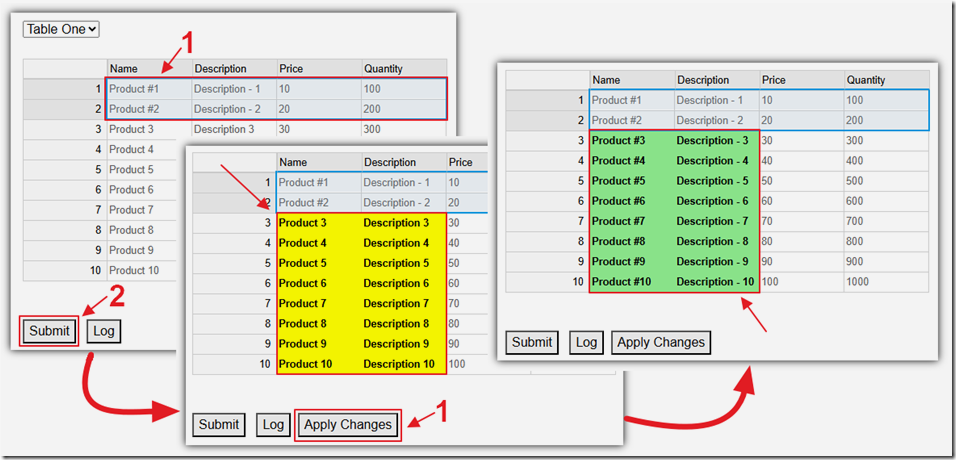
-
Blazor & OpenAI Integration: Discusses integrating Microsoft Blazor with the data editor and OpenAI’s LLM model to enhance data management within a Blazor application.
-
AI-Powered Data Edits: It showcases how AI can infer rules from user edits and apply them to other data entries, such as adding missing area codes to phone numbers.
-
Implementation Steps: The article provides a step-by-step guide on setting up the necessary NuGet packages, configuring services, and adding code to a Blazor project to utilize the OpenAI model.
-
Resulting Functionality: By using the OpenAI model, the application can automatically highlight and suggest changes to data, which users can then apply to ensure data consistency and accuracy.
Download
The project is available at the following location: https://github.com/ADefWebserver/BlazorDatasheet
You must have Visual Studio 2022 (or higher) installed to run the code.