1/3/2024 Admin
Godot and Microsoft Blazor
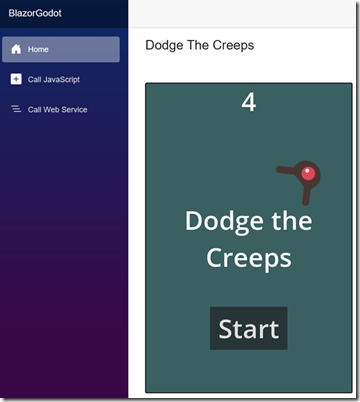
Blazor is a web framework that allows developers to build interactive web applications using C# and HTML. It provides a server-side hosting model where Blazor is executed on the server from within an ASP.NET Core app. This hosting model allows Blazor to handle user management and securely communicate with external resources like large language model APIs.
Godot is a free and open-source game engine that allows developers to create 2D and 3D games with various languages and features. It is designed to support all sorts of projects and can be used to create games or applications that can be released on desktop or mobile, as well as on the web.
In this blog post, we will cover the following topics:
- Hosting a Godot application in Blazor and dynamically loading the required JavaScript files.
- We will also discuss how to communicate with Blazor from Godot using JavaScript and securely call Blazor from Godot
- Finally, we will also discuss how to communicate with Blazor from Godot using web services and receive and display a JSON response.
Live Demonstration
You can access the live demonstration at this link: https://blazorgodot.azurewebsites.net/
Note: It only works in Chromium web browsers (Google Chrome/Microsoft Edge). It doesn’t work on Safari or Firefox.
The Source Code
- https://github.com/ADefWebserver/BlazorGodot – GitHub source code for the Blazor project
- https://github.com/godotengine/godot-demo-projects/tree/master/2d/dodge_the_creeps – GitHub source code for the Godot Dodge The Creeps Game
- GoDotSourceFiles1-2024.zip (stored at the link: “Godot and Microsoft Blazor”) – Godot source code for Blazor JavaScript and BlazorWebService projects
How It Works
- Export your Godot app as HTML5
- Place the exported files in the Blazor app
- Dynamically load the required JavaScript files
Notes
- To create HTML5 output in Godot 4.2, you need to use the non-.NET version of Godot
- You must add custom MIME mapping to serve the Godot .pck files in the program.cs file of the Blazor application
- The Godot HTML5 app requires support for SharedArrayBuffer. To do this you must set Response.Headers using coi-serviceworker.js
- When you deploy your Blazor site to Azure, the calls made using the Godot HTTPRequest node will fail with a "core/io/stream_peer_gzip.cpp:117" error. It seems that the problem was caused by the “Accept Gzip” option being enabled on your HTTPRequest node. Unchecking the box should fix the issue.
The Samples
We will now cover the three samples…
Loading a Godot App in Blazor – Export Godot app as a HTML 5 App
First we load the Dodge The Creeps Game Godot App.
We select Export.
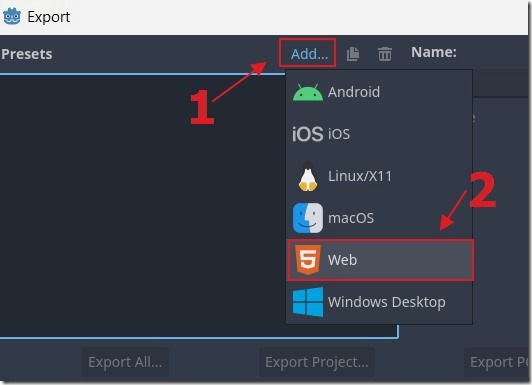
We select Add then the Web template.
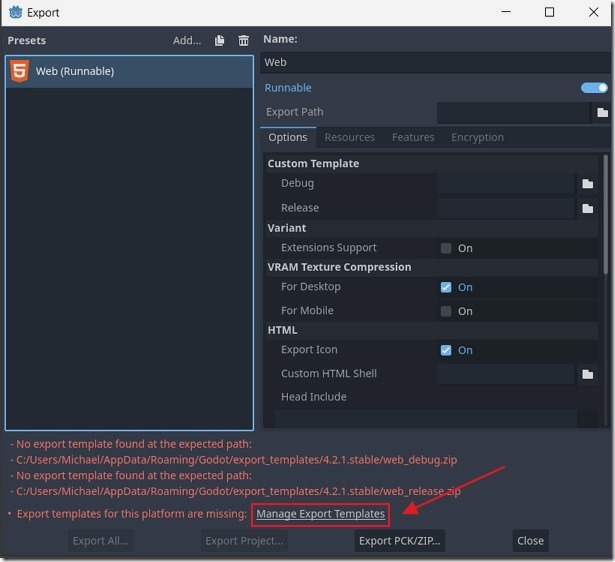
If the Export templates have not been downloaded, we click the button to download them now.
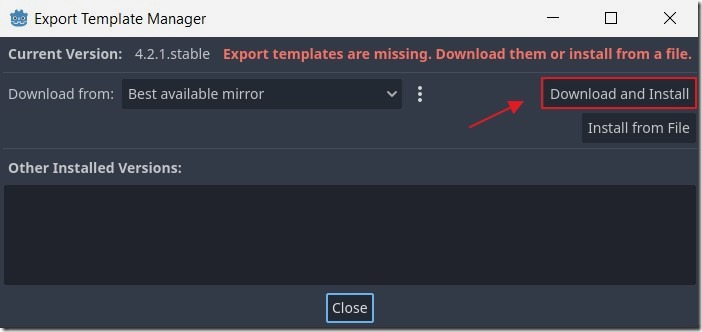
We then click the Download and Install button.
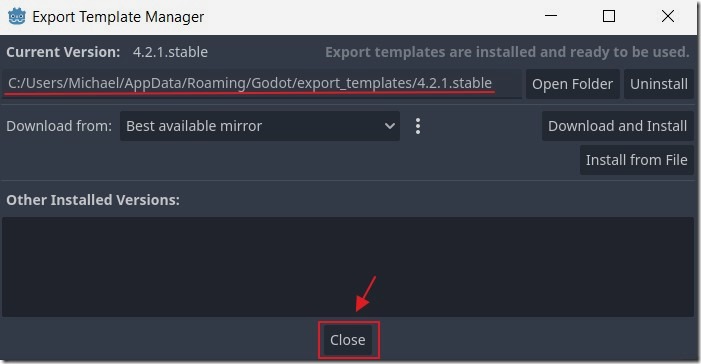
When the Export templates have been downloaded we click the Close button.
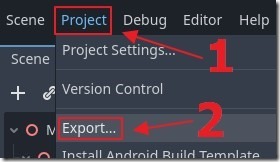
We can now select Export again.
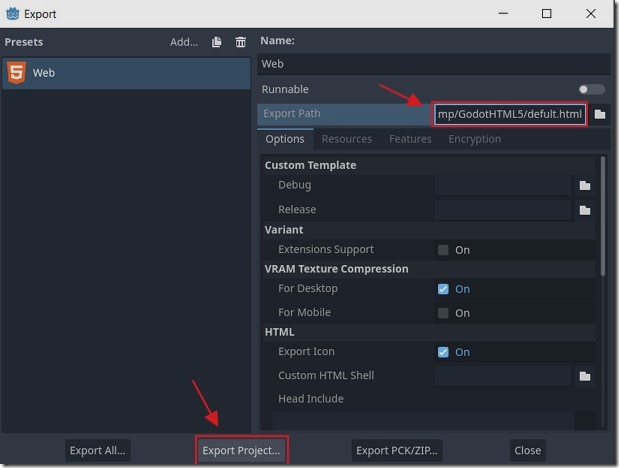
We can now set an Export Path where we want the HTML 5 to be exported to and click the Export Project button.
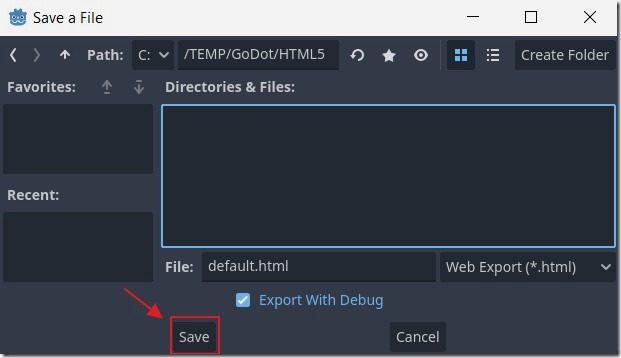
Give the HTML file a name and click the Save button.
Loading a Godot App in Blazor – The Blazor App
The source code for the Blazor application is located in GitHub at:
https://github.com/ADefWebserver/BlazorGodot
To handle serving the Godot .pck files we must add custom MIME mapping in the program.cs file of the Blazor application using the following code:
var provider = new FileExtensionContentTypeProvider();// Add new mappingsprovider.Mappings[".pck"] = "application/octet-stream";app.UseStaticFiles(new StaticFileOptions{ContentTypeProvider = provider});
Also, the Godot HTML5 app requires support for SharedArrayBuffer. To do this we must set Response.Headers using: https://github.com/gzuidhof/coi-serviceworker
Add the JavaScript file to the root of the wwwroot directory.
Add the following script reference to the App.razor page:
<script src="coi-serviceworker.js"></script>
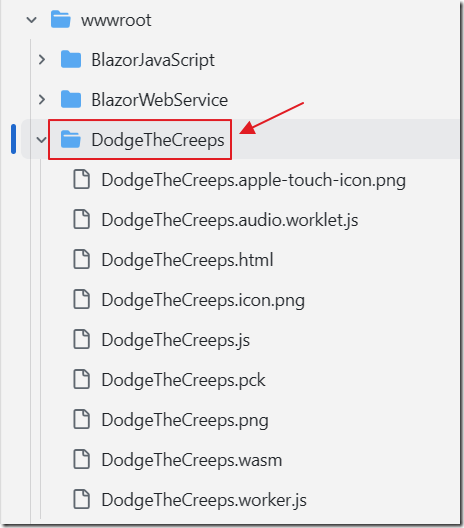
All the HTML 5 files exported earlier have been placed in a folder called DodgeTheCreeps under the wwwroot folder.
The root HTML web page of the Blazor application is the App.razor page.
This page contains the CSS styles required by the Godot apps and the following JavaScript to load the Godot app:
<script>window.GodotApp = {showApp: function (canvasElement, godotApplicationName, godotArgs) {const GODOT_CONFIG = {"args": godotArgs,"canvasResizePolicy": 1,"executable": godotApplicationName,"experimentalVK": false,"focusCanvas": true,"gdextensionLibs": []};const engine = new Engine(GODOT_CONFIG);const INDETERMINATE_STATUS_STEP_MS = 100;const statusProgress = document.getElementById('status-progress');const statusProgressInner = document.getElementById('status-progress-inner');const statusIndeterminate = document.getElementById('status-indeterminate');const statusNotice = document.getElementById('status-notice');let initializing = true;let statusMode = 'hidden';let animationCallbacks = [];function animate(time) {animationCallbacks.forEach((callback) => callback(time));requestAnimationFrame(animate);}requestAnimationFrame(animate);function animateStatusIndeterminate(ms) {const i = Math.floor((ms / INDETERMINATE_STATUS_STEP_MS) % 8);if (statusIndeterminate.children[i].style.borderTopColor === '') {Array.prototype.slice.call(statusIndeterminate.children).forEach((child) => {child.style.borderTopColor = '';});statusIndeterminate.children[i].style.borderTopColor = '#dfdfdf';}}function setStatusMode(mode) {if (statusMode === mode || !initializing) {return;}[statusProgress, statusIndeterminate, statusNotice].forEach((elem) => {elem.style.display = 'none';});animationCallbacks = animationCallbacks.filter(function (value) {return (value !== animateStatusIndeterminate);});switch (mode) {case 'progress':statusProgress.style.display = 'block';break;case 'indeterminate':statusProgress.style.display = 'block';statusIndeterminate.style.display = 'block';animationCallbacks.push(animateStatusIndeterminate);break;case 'notice':statusNotice.style.display = 'block';break;case 'hidden':break;default:throw new Error('Invalid status mode');}statusMode = mode;}function setStatusNotice(text) {while (statusNotice.lastChild) {statusNotice.removeChild(statusNotice.lastChild);}const lines = text.split('\n');lines.forEach((line) => {statusNotice.appendChild(document.createTextNode(line));statusNotice.appendChild(document.createElement('br'));});}function displayFailureNotice(err) {const msg = err.message || err;console.error(msg);setStatusNotice(msg);setStatusMode('notice');initializing = false;}const missing = Engine.getMissingFeatures();if (missing.length !== 0) {const missingMsg = 'Error\nThe following features required to run Godot projects on the Web are missing:\n';displayFailureNotice(missingMsg + missing.join('\n'));} else {setStatusMode('indeterminate');engine.startGame({'canvas': canvasElement,'onProgress': function (current, total) {setStatusMode('progress');var progress = (current / 99999999);if (progress > 0.99999999) {progress = 0.99999999;}statusProgressInner.style.width = `${(current / 99999999) * 100}%`;// wait for progress bar animationsetTimeout(() => {setStatusMode('indeterminate');}, 500);},}).then(() => {setStatusMode('hidden');initializing = false;}, displayFailureNotice);}}}</script>
The Dodge The Creeps Godot app is loaded on the Home.razor page.
It uses the following HTML to display a canvas element and a Load App button to load the app:
@page "/"@rendermode InteractiveServer@inject IJSRuntime JSRuntime<PageTitle>Home</PageTitle><h4>Dodge The Creeps</h4><button class="btn btn-primary" hidden=@LoadButtonVisible @onclick="LoadApp">Load App</button><br><br><canvas @ref="@GodotCanvas" id="canvas-element" style="width:100%;height:600px;max-width: 2000px"><p>HTML5 canvas appears to be unsupported in the current browser.</p><p>Please try updating or use a different browser.</p></canvas><div id="status"><div id="status-progress" style="display: none;" oncontextmenu="event.preventDefault();"><div id="status-progress-inner"></div></div><div id="status-indeterminate" style="display: none;" oncontextmenu="event.preventDefault();"></div><div id="status-notice" class="godot" style="display: none;"></div></div>
The following C# code dynamically loads the required JavaScript files:
@code {private ElementReference GodotCanvas;bool LoadButtonVisible = false;string GodotApplicationName = "DodgeTheCreeps/DodgeTheCreeps";string GodotArgs = "[]";// method to run on load of pageprotected override async Task OnAfterRenderAsync(bool firstRender){if (firstRender){await LoadScript(GodotApplicationName + ".js");}}async Task LoadScript(string paramGodotApplicationScript){var script = await JSRuntime.InvokeAsync<IJSObjectReference>("eval", "document.createElement('script')");await script.InvokeVoidAsync("setAttribute", "src", paramGodotApplicationScript);await script.InvokeVoidAsync("setAttribute", "type", "text/javascript");await script.InvokeVoidAsync("setAttribute", "async", "");await script.InvokeVoidAsync("setAttribute", "defer", "");await JSRuntime.InvokeVoidAsync("document.body.appendChild", script);}}
The following C# code responds to the user clicking the Load App button:
private async Task LoadApp(){LoadButtonVisible = true;await Interop.CreateGodotApp(JSRuntime,GodotCanvas,GodotApplicationName,GodotArgs);}
This calls the following code that calls the JavaScript on the App.razor page:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components;using Microsoft.JSInterop;using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace BlazorGodot{public static class Interop{internal static ValueTask<object> CreateGodotApp(IJSRuntime jsRuntime,ElementReference GodotCanvas,string GodotApplicationName,string GodotArgs){return jsRuntime.InvokeAsync<object>("GodotApp.showApp",GodotCanvas,GodotApplicationName,GodotArgs);}}}
When we run the Blazor application, we can click the Load App button…
The app will load.

We can then click Start to play the game.
Note: It requires a keyboard to play. Use the W A S and D keys.
Godot and JavaScript
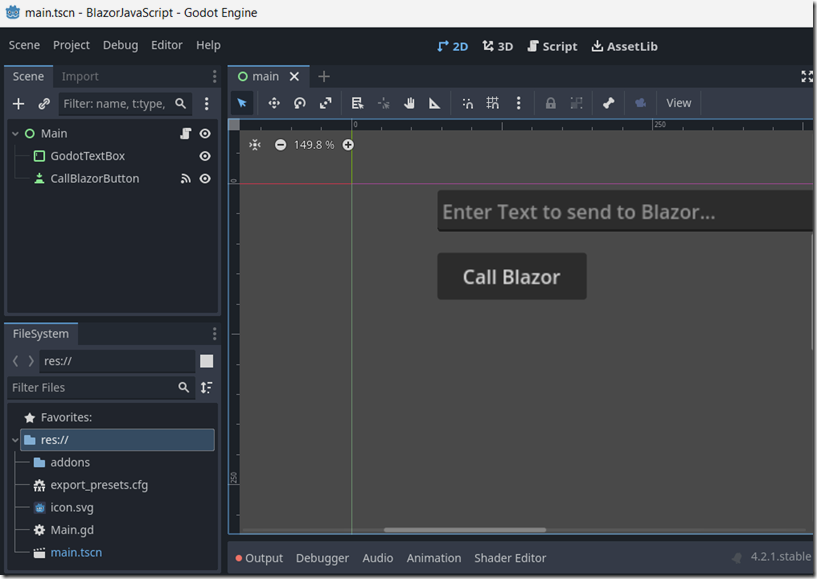
The next sample demonstrates how Godot can call a custom Blazor JavaScript method that passes a value to server side Blazor code.
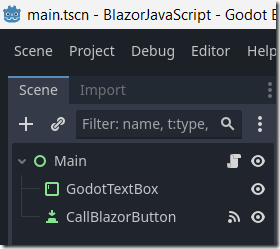
There is only a single Godot scene that has a TextBox and a Button.
When the button is pressed, this GDScript method calls the receiveCalFromGodot Blazor JavaScript method, passing the contents of the TextBox:
func _on_call_blazor_button_pressed():# Get the GodotTextBox nodevar godotTextBox = $GodotTextBox# Call JavaScriptJavaScriptBridge.eval("receiveCallFromGodot('" + godotTextBox.text + "');")
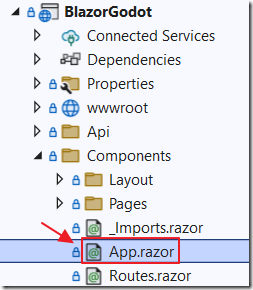
In Blazor, the receiveCalFromGodot Blazor JavaScript method is contained on the App.razor page:
<script>window.receiveCallFromGodot = async (godotMessage) => {DotNet.invokeMethodAsync('BlazorGodot', 'ReceiveCallFromGodot', godotMessage).then((result) => {alert(result);}).catch((error) => {console.log("Error: ", error);});};</script>
This method calls the following server side C# Blazor method (contained on the \Components\Pages\CallJavaScript.razor page):
[JSInvokable("ReceiveCallFromGodot")]public static Task ReceiveCallFromGodot(string godotMessage){string response = $"Response from Server Side Blazor: You sent {godotMessage} ({godotMessage.Length} characters).";return Task.FromResult(response);}
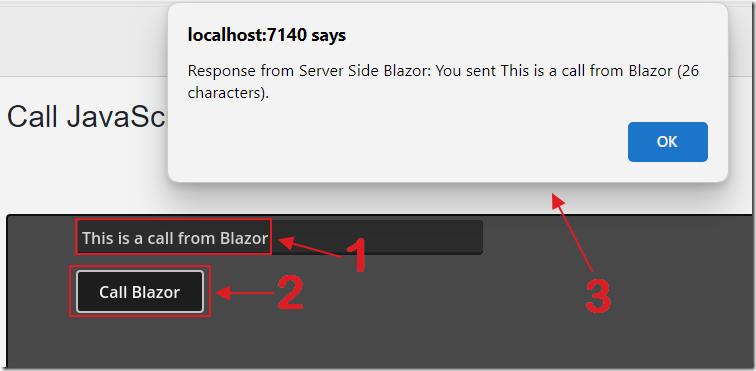
The receiveCalFromGodot Then displays the result in a JavaScript popup.
Godot and Web Services
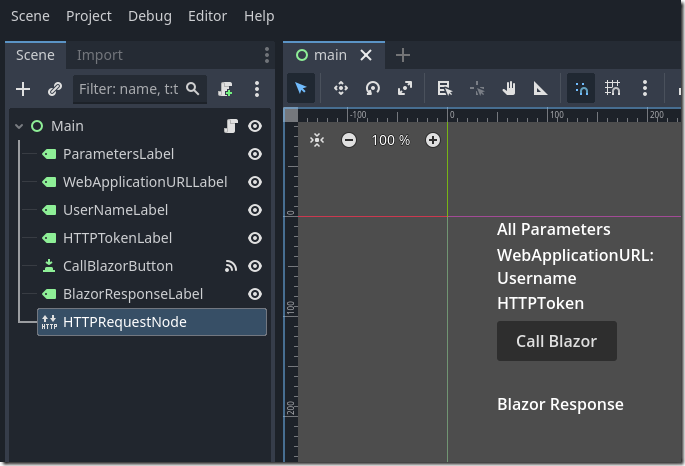
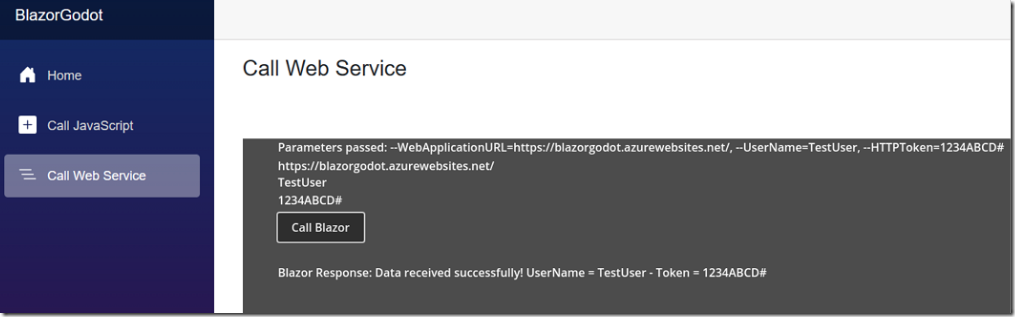
The final sample demonstrates how Godot can call a Blazor Web Service method. The Godot code receives a Username and a HTTPToken as starting parameters from the Blazor application, and then passes these values to the Blazor web service method, and receives a response.
The Username and a HTTPToken, in a real application can be used by the Blazor application to validate the call to its web service.
The following GDScript method receives the parameters passed to it on startup:
func _ready():#Get controlsvar ParametersLabelControl = $ParametersLabelvar WebApplicationURLControl = $WebApplicationURLLabelvar UserNameLabelControl = $UserNameLabelvar HTTPTokenLabelControl = $HTTPTokenLabel# Define the variablesvar text_to_display = ""var WebApplicationURL = ""var paramUserName = ""var paramHTTPToken = ""var cmdline_args = OS.get_cmdline_args()#var FirstArguments = "--WebApplicationURL=https://blazorgodot.azurewebsites.net/,--UserName=TestUser,--HTTPToken=1234ABCD#"var FirstArguments = cmdline_args[0]var FirstArgumentsArray = FirstArguments.split(",")# Get all for text_to_displayfor arg in FirstArgumentsArray:text_to_display += arg + ", "# Remove the last comma and space if there are any argumentsif FirstArgumentsArray.size() > 0:text_to_display = text_to_display.substr(0, text_to_display.length() - 2)# Set UserName and HTTPTokenfor i in range(FirstArgumentsArray.size()):if FirstArgumentsArray[i].begins_with("--WebApplicationURL"):var AllKeyParts = FirstArgumentsArray[i].split('=', true, 1)WebApplicationURL = AllKeyParts[1]if FirstArgumentsArray[i].begins_with("--UserName"):var AllKeyParts = FirstArgumentsArray[i].split('=', true, 1)paramUserName = AllKeyParts[1]if FirstArgumentsArray[i].begins_with("--HTTPToken"):var AllKeyParts = FirstArgumentsArray[i].split('=', true, 1)paramHTTPToken = AllKeyParts[1]ParametersLabelControl.text = "Parameters passed: " + text_to_displayWebApplicationURLControl.text = WebApplicationURLUserNameLabelControl.text = paramUserNameHTTPTokenLabelControl.text = paramHTTPToken
When the Call Blazor button is clicked the following code is used:
func _on_call_blazor_button_pressed():var http_request = $HTTPRequestNodevar WebApplicationURLControl = $WebApplicationURLLabelvar UserNameLabelControl = $UserNameLabelvar HTTPTokenLabelControl = $HTTPTokenLabel# Connect the request_completed signal#http_request.connect("request_completed", Callable(self, "_on_request_completed"))#http_request.connect(self._http_request_completed)http_request.request_completed.connect(self._on_request_completed)# Prepare data to sendvar user_name = UserNameLabelControl.textvar http_token = HTTPTokenLabelControl.text# Send POST requestvar url = WebApplicationURLControl.text + "ReceiveCallFromGodot/"var body_dict = {"userName": user_name,"hTTPToken": http_token}var json = JSON.new()var body = json.stringify(body_dict)var headers = ["Content-Type: application/json"]http_request.request_completed.connect(self._on_request_completed)var error = http_request.request(url, headers, HTTPClient.METHOD_POST, body)if error != OK:print("Error sending request: ", error) # Print the specific error code
When the Blazor web service response comes back, the following code is used to process the response:
func _on_request_completed(result, response_code, headers, body):var BlazorResponseLabelControl = $BlazorResponseLabel# Check the response codeif response_code == 200:var body_string = body.get_string_from_utf8()print("Raw response body: ", body_string)BlazorResponseLabelControl.text = "Blazor Response: " + body_stringvar json = JSON.new()var parsed_data = JSON.parse_string(body_string)print("Parsed JSON data: ", parsed_data)# Accessing the message field in the JSON objectif typeof(parsed_data) == TYPE_DICTIONARY and "message" in parsed_data:var message = parsed_data["message"]print("Message: ", message)BlazorResponseLabelControl.text = "Blazor Response: " + messageelse:print("Unexpected JSON structure")
In the Blazor CallWebService.razor page the following highlighted code passes the parameters to the Godot app when it loads:
string GodotApplicationName = "BlazorWebService/BlazorWebService";string GodotArgs = "";protected override void OnInitialized(){// get the base url of the current pagevar baseURI = NavigationManager.BaseUri.Replace("https://", "").Replace("http://", "").Replace("/", "");GodotArgs = @$"--WebApplicationURL=https://{baseURI}/,--UserName=TestUser,--HTTPToken=1234ABCD#";}private async Task LoadApp(){LoadButtonVisible = true;await Interop.CreateGodotApp(JSRuntime,GodotCanvas,GodotApplicationName,GodotArgs);}
Deploying to Azure
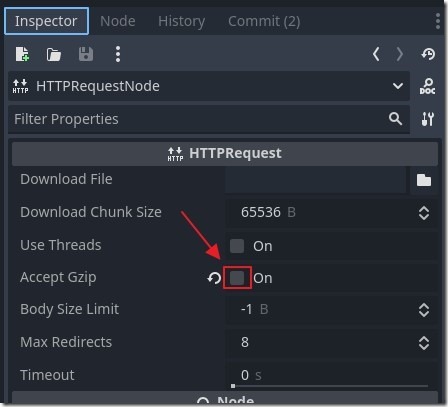
When you deploy your Blazor application to Azure, the calls made using the Godot HTTPRequest node may fail with a "core/io/stream_peer_gzip.cpp:117" error. It seems that the problem is caused by the “Accept Gzip” option being enabled on your HTTPRequest node. Unchecking the box should fix the issue.
Links
Download
The GoDot projects are available on the Downloads page on this site.
